COSAM » Departments » Chemistry & Biochemistry » Facilities » massspec » Learn about mass spectrometry » MALDI-TOF » Time of Flight
Kinetic Energy (KE) = 1/2*mass*velocity2
KE = 1/2mv2
or
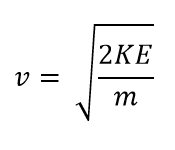
Then the time in the flight tube is related to the length (or distance) of the flight tube.
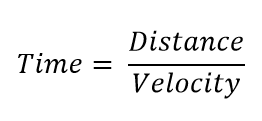
Substitute velocity (v) to get

Simplify and we see that the flight time is proportional to the square root of the mass of the ions. Notice the ion kinetic energy is also important. We will discuss this more in the reflectron section.
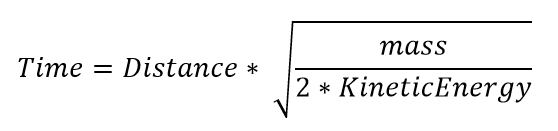
Last Updated: 05/17/2019
